Jan 21 2016
In a storage ring like BESSY II electrons circulate nearly with the speed of light passing complex magnetic structures. These magnets guide the electron beam and focus it on the ideal orbit.
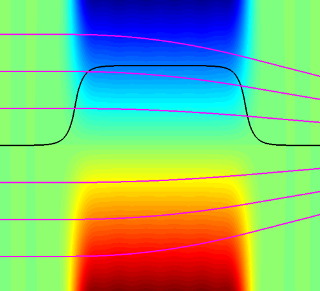 Vertical cut through a quadrupole magnet: Black: Field distribution at a fixed vertical distance to the midplane. Magenta: Electron trajectories for various initial coordinates. Credit: C. Rethfeldt/HZB
Vertical cut through a quadrupole magnet: Black: Field distribution at a fixed vertical distance to the midplane. Magenta: Electron trajectories for various initial coordinates. Credit: C. Rethfeldt/HZB
They are comparable to optical lenses which focus the light. To evaluate the stability of the electron trajectories in the magnetic fields, several thousands of turns need to be simulated. After each revolution the trajectories are slightly different, passing the magnets at slightly different positions. These combined and complex orbit and field calculations require a precise algorithm which could easily result in time consuming simulations.
Already in 2011, a team out of the HZB undulator group and of the HZB-institute of accelerator physics has published a first paper of a new simulation algorithm, which drastically speeds up the simulation time for trajectories in complex undulator fields. This simulation routine was implemented into the public domain code "elegant" of the Advanced Photon source / Argonne, and it is available, worldwide.
Now, the young scientist Malte Titze together with the senior scientists Johannes Bahrdt and Godehard Wüstefeld could extend this method to another important class of three dimensional magnets: multipoles such as quadrupoles or sextupoles.
"The paper demonstrates, that this method yields very precise results, particularly within the fast changing fringing fields of the magnets", Malte Titze explains. He is now engaged in research activities at CERN. "Such simulation methods are of great interest for future light sources, especially for diffraction limited storage rings, which may include combined function magnets and exhibit significant cross talking between neighboring magnets" comments Johannes Bahrdt. "This is of clear relevance for a successor of BESSY II". The scientists describe their methods in the renowned journal of Physical Review Special Topics Accelerator & Beams.
Source: https://www.helmholtz-berlin.de/